When your business uses a cloud service like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365, you may be unaware of a “shared responsibility” that exists between your company and the cloud vendor for your data.
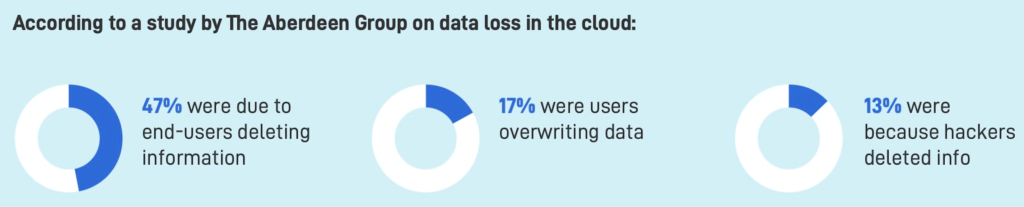
Many companies are not aware of their responsibility to backup their cloud data. If you read the fine print in your subscription agreement, both Google and Microsoft make very clear about each party’s share of responsibility. They point out that there are a number of areas that are outside of the cloud vendors’ control and that are within your control.
In this post, we’ll look at the shared responsibility model and help you understand what’s covered by the vendor and what is not.
We’ll also look at ways you can manage your business’s share of the responsibility.
The Vendors’ Share of Responsibility
The cloud vendors such as Google and Microsoft are responsible for the following areas:
1. Physical and electronic security in their data centers
The vendors need to prevent unauthorized physical or electronic entry into the data centers where your business data is housed. Only they can secure the perimeter of the data centers and doorway entry into the centers.

2. Uptime and performance of their servers
Cloud vendors need to keep servers and other equipment running. They need to maintain enough computing power to ensure well-performing services for their customers.
3. Working applications such as Google Sheets or Microsoft PowerPoint
Other than file storage, the main reason for subscribing to these vendors’ services is to benefit from the efficiencies and collaboration that their SaaS (Software as a Service) applications bring to your business.
The vendors have to provide for user login access to applications and files. But this is where their responsibility ends and where your responsibility as a customer begins.
Your Company’s Share of Responsibility
Neither Google nor Microsoft are ultimately responsible for your data.
You are responsible for your user accounts or the identities of your users.
You are responsible for endpoint protection of your company’s devices.
Your Employees and Your Devices
Neither Google nor Microsoft can stop your employees or contractors from trashing emails and files. Nor can these vendors prevent a company-owned device from being taken over by an intruder or a thief.
Your User Accounts and Identities
You are responsible for who you give access to, the strength of your security settings and what those users do with the data.
Your Microsoft Office 365 or Google Workspace administrator creates accounts for your users. An administrator also sets certain security policies.
Your company or your MSP is responsible for training users and/or enforcing two important user-level security components:
1. Password management and encouraging the use of strong passwords
2. Multi-factor authentication
A weak password with no form of authentication beyond the password itself gives a would-be hacker easy access to your company data where it can be deleted, corrupted or stolen.
Your Devices
Computers, tablets and mobile devices used for work can be viewed as the gateways to your data in the cloud. As such, they fall into your side of shared responsibility. Proper endpoint protection should be implemented company-wide.
The following infographic summarizes a business’s share of the responsibility:
When You Wished You Had a Backup
Important as they are, strong passwords and multi-factor authentication will not prevent human actions or errors. Here are some examples of scenarios in which data should be or must be recovered.
- Jim accidentally deleted a file two months ago. You need a copy of the file from before the change or deletion.
- Jennifer left the company. You want to transfer all of the former employee’s email history into someone else’s mailbox.
- Jim’s computer was crypto-locked. The locked files were all synced up to Google Shared drives or to Microsoft OneDrive. The unlocked cloud files were overwritten with locked files.
- Your company’s entire accounting folder was crypto-locked.
- For legal reasons, your CEO needs to restore an email from years ago that she long since deleted from her account.
A Big Misconception: Cloud Data is Forever
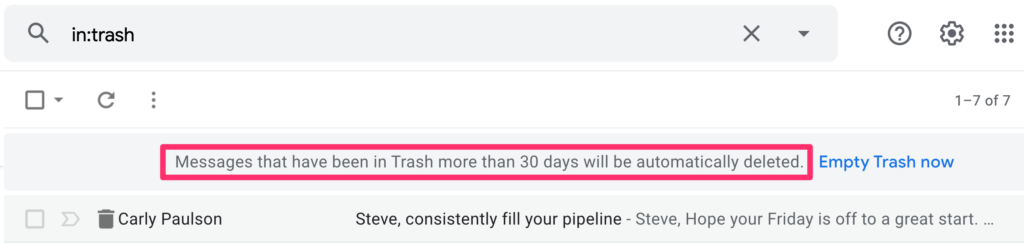
Guess what? It is not. When a file is moved to the trash (a.k.a. deleted) it stays in the trash bin for a little while and then “poof” it is gone FOREVER.
Google has a simple retention policy. Emails and files that a user trashes are permanently deleted after 30 days.
With Microsoft, generally speaking, there is a 93-day retention period for Sharepoint and OneDrive files that are moved to the recycle bin.
How To Protect Your Cloud Data
With so much critical business data being stored in the cloud today, it is imperative that it is backed up regularly and easily recoverable. There are a variety of cloud-to-cloud backup solutions available that will ensure your Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 files and emails are securely backed up to a secondary cloud provider.
A cloud-to-cloud backup solution stores your data in a structured manner. This allows for fast restores.
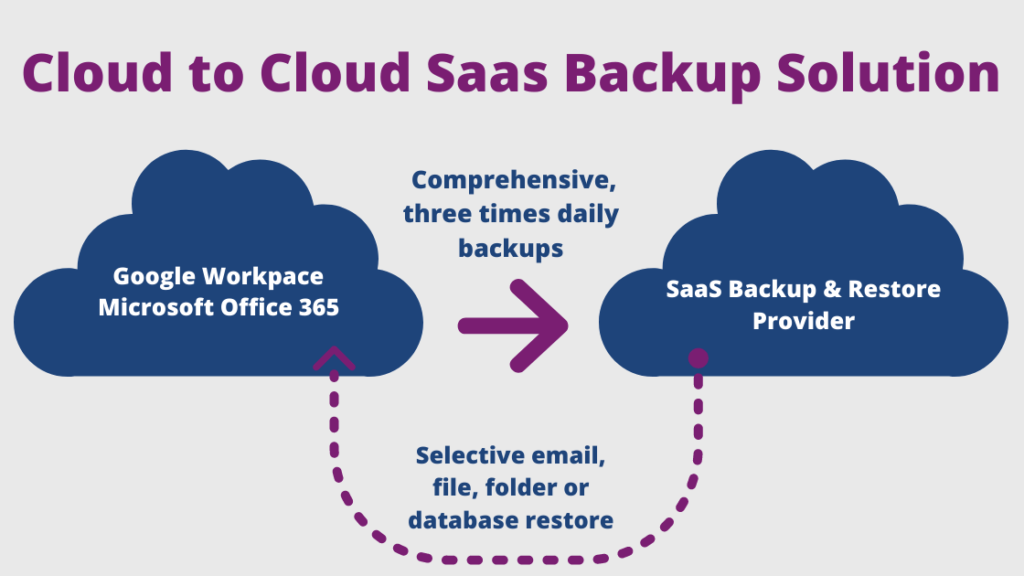
These solutions take a “snapshot” of your cloud data every few hours and copy the data to a separate, secure cloud location. This makes it a snap to restore any email message, file, folders or cloud drive.