Before moving to a new office space, it’s a good idea to find out if your business communications lifeline — the location’s business internet service options — is sufficient for your employee count and how the internet will be used.
How internet service is physically delivered to a building correlates to upload and download speeds. That’s why a business owner or executive should know the information below.
How Internet Speed is Measured
Business internet speed is measured in millions or billions of bits per second. “Mbps” means one million bits per second. “Gbps” means one billion bits per second.
If you search “internet speed test” on Google and then run a test, you will see both a download and upload speed for your location.
Example Bandwidth Requirements
Here are the bandwidth requirements for Google Meet, a popular business tool:
Each participant must have a 3.2 Mbps upload bandwidth. Download requirements depend on the number of participants:
- 2.6 Mbps for 2 participants
- 3.2 Mbps for 5 participants
- 4.0 Mbps for 10 participants
Watching a 720p YouTube video uses roughly 0.25 Mbps. So, ten people watching a 720p video simultaneously would require about 25 Mbps.
Download vs. Upload Speeds
Some delivery methods are asymmetrical, which means they have much higher download speeds than upload speeds. Other business internet service types are symmetrical, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same.
If your employees upload many large files (like videos), symmetrical service will result in higher productivity.
Business Internet Service Delivery Methods
There are six main ways internet service can be physically delivered to a business’s premises. Upload and download speeds vary based on how much a business is willing to pay.
The top-end speed of a given delivery method is ultimately constrained by physics. However, internet service providers continually engineer ways to move closer to the constraints of the physical medium.
1. Solid Core Copper Wire
Twisted-pair copper wire dominated the communications infrastructure during the 20th century. It was the physical delivery method for telephone service to homes and businesses.
Data was carried over solid core copper telephone wire for decades as a DSL (Digital Subscriber Loop) service. However, because of the type of wiring that carries the signal, DSL is physically limited in speed, even under ideal conditions. Furthermore, in less-than-ideal conditions, such as old copper wiring jackets that moisture can penetrate, DSL can become even more limited.
Business internet service providers are understandably moving away from twisted-pair copper wire.
Example high-end DSL speed: 400 Mbps down & 8 Mbps up
2. Fixed Wireless
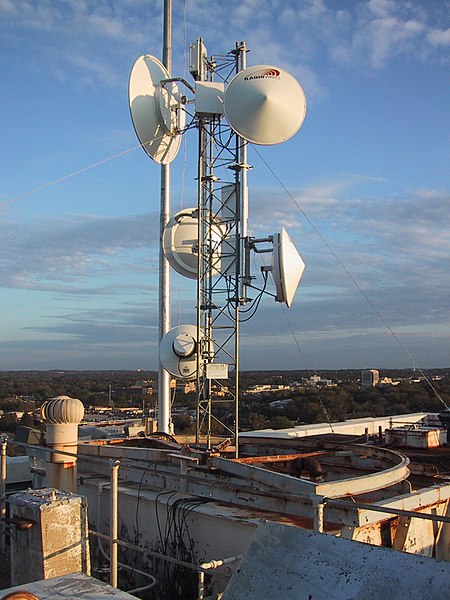

Fixed wireless business internet services are sometimes offered in areas where it is difficult to get an affordable or decent internet connection from a terrestrial internet service provider.
Companies looking for a second internet carrier can add fixed wireless alongside an existing land-based provider.
This delivery method requires a line-of-sight connection from a radio tower to a business’s rooftop.
Example business fixed wireless high-end speed: 50 Mbps down & 20 Mbps up
3. Satellite

Satellite internet delivery was once an uncommon option for most businesses because of its relatively high latency and low speeds.
With first-generation satellite service, data traveled a long distance. First, it had to go to space and back to Earth—almost 23,000 miles each way. This caused noticeable lags with interactive internet communications such as VoIP phone calls.
SpaceX’s Starlink division changed how satellite internet is delivered with its business offering. The Starlink satellites’ orbit is about 340 miles above the Earth’s surface. This means a relatively low latency of 25 to 60 milliseconds.
The Starlink website says users can expect up to 220 Mbps download speed and 25 Mbps upload speed. In addition, a business can order as many Starlink kits as it needs and manage them from a centralized account.
4. Coaxial Cable

Most people are familiar with coaxial (a.k.a. coax) cable as the cylindrical black or white-jacketed cable connected to the back of their cable TV box.
The same type of cable carries internet service to many office buildings. Coax speeds are generally faster than that of copper or fixed wireless. Comcast Business is the leading provider of coax-based internet services.
A technology called DOCSIS 3.1 increased the bandwidth of coax cables. However, coax download speeds are much faster than upload speeds.
Example business coax cable high-end speed: 1 Gbps down & 35 Mbps up.
5. Cellular Wireless

Cellular carriers provide a wireless internet option to businesses near cellular towers. For example, Verizon offers Fios Business Internet. This service is symmetrical or near-symmetrical.
AT&T offers Wireless Broadband as an alternative to traditional broadband service for small businesses.
Example cellular high-end speed: 940 Mbps up & 880 Mbps down
6. Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cable service is the fastest business internet service option available.
As its name implies, information is transmitted optically through light waves. Signals travel at close to the speed of light. Fiber optic cable can deliver up to 100 Gbps—one hundred billion bits per second.
Fiber optic service is mainly symmetrical — the upload and download speeds are the same.
There is a wide range of bandwidth offerings and associated price levels. AT&T fiber customers, for example, can choose from packages ranging from 100 Mbps to 5 Gbps or more.
Example business fiber optic high-end speed: 5 Gbps up & 5 Gbps down
Ensuring high network availability
If you plan to move your business to a new location, it’s worth finding out if more than one internet service provider has a connection to the new site.
Why more than one provider?
An increasing number of companies subscribe to two business internet service providers. With a specialized router in place, the result is a total speed that is the sum of the rates of two providers. This also means high internet service availability, as there is continuity should one provider’s connection fail.


