Patching your business’s software and devices is an essential defense against ransomware attacks and other malicious intrusions.
According to Wikipedia, “In computer security, a vulnerability is a weakness which can be exploited by a threat actor, such as an attacker, to cross privilege boundaries (i.e., perform unauthorized actions) within a computer system.”
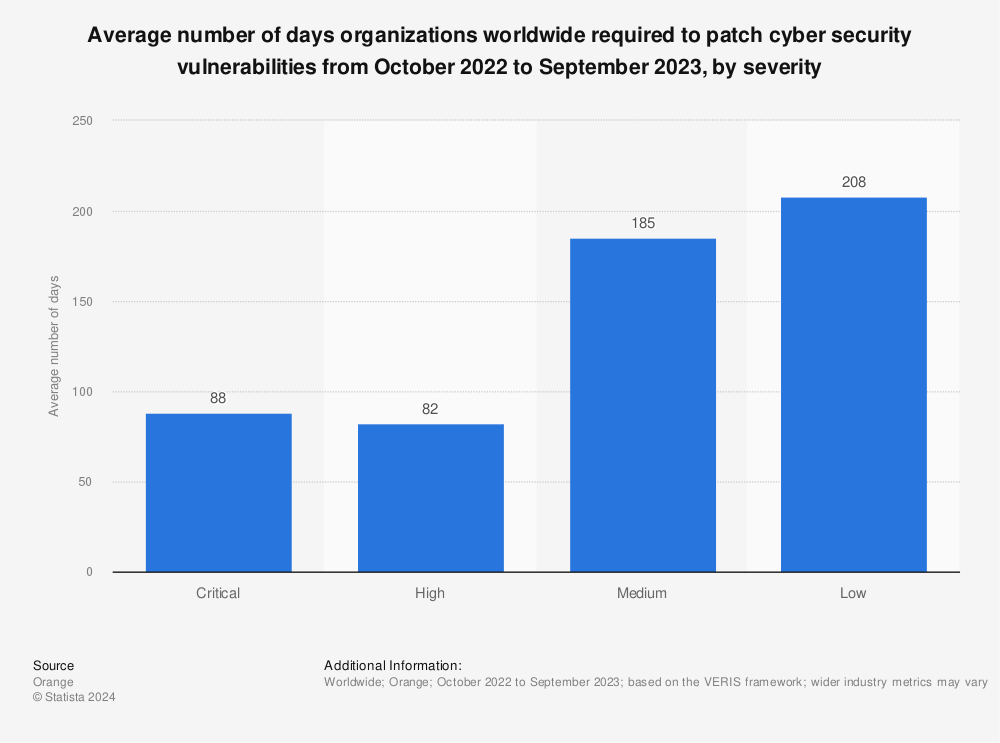
According to a survey conducted by Orange Cyberdefense, organizations, on average, take 88 days to patch critical cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
With the proliferation of operating systems and devices, business environments require a wider range of — and more frequent — software patching than ever before.
This is why many organizations implement patch management software.
Vulnerabilities are such a pervasive problem that a centralized database has many contributors.
Most known software and device (firmware) vulnerabilities are assigned a unique identifier called a CVE. CVE stands for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures.
The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a searchable online database that “contains the most recent CVE cyber vulnerabilities published within the National Vulnerability Database.”
Until your internal IT department or your organization’s managed IT service provider has a mechanism to patch most of your systems automatically, you and your employees may need to be more vigilant than ever about manually installing security updates.
Computers and network devices sometimes have software that can no longer be updated without extra costs. In those cases, you should consider replacing the software or the device.
“60% of breach victims said they were breached due to an unpatched known vulnerability where the patch was not applied.”
– 2019 Poneman Institute Survey
Here is a list of software and hardware devices subject to CVEs and needing periodic (sometimes frequent) patching.
Desktop operating systems
Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux must be patched or updated continually.
Microsoft Windows has monthly security updates, which are cumulative. The monthly security release includes all security fixes for Windows vulnerabilities and non-security updates.
Usually, desktop operating systems should be patched as soon as possible after a new patch is released. However, there are occasional exceptions. For example, some Windows patches have been known to cause more problems than they solved. The role of a managed IT service provider is to make this determination for their customers.
It’s worth mentioning that there are many unpatched Windows 7 machines since Windows 7 users no longer get free security updates from Microsoft. Microsoft says, “If you continue to use Windows 7 after support has ended, your PC will still work, but it will be more vulnerable to security risks and viruses.”
Server operating systems
If you have in-house or colocated servers in your business, their operating systems are vulnerable.
An intruder often compromises desktop operating systems such as Windows 10 to access a Windows server OS, where ransomware can be executed.
Windows Server 2008 is in a similar position to Windows 7. Server 2008 is past end-of-life, but ESUs can be purchased for now.
Mobile OSs
Whether a mobile device is company-owned or a BYOD, the operating system should be updated as soon as security patches and new versions are available.
Apple has a page dedicated to security releases.
When an iPhone or Android device is too old to be updated to the current release, you should consider replacing the device.
Desktop software applications
Desktop applications are not immune from security issues.
Popular software such as Microsoft Office, Adobe Flash, and Apple’s QuickTime Player have all been known to have vulnerabilities.
Physical server software
Applications such as Microsoft Sharepoint Server and Microsoft Exchange Server are also subject to vulnerabilities.
Virtual server software
Regarding potential vulnerabilities, virtual servers are no different from physical servers.
Software patches should be applied to virtual server software as soon as possible after being released and vetted by your IT department or managed IT service provider.
Mobile apps
Older software applications that are not updated regularly on mobile devices are targets for software security issues.
Users should pay attention to the update-notifier on their mobile devices.

Antivirus and anti-malware software
In addition to applying patches for business productivity software on your computer, you should regularly update antivirus software.
Most anti-malware software is updated automatically. However, it is possible that the software may not update itself if the software manufacturer’s servers are offline.
Web browsers
Most of today’s web browsers are self-patching through automatic updates.
Chrome, for example, automatically downloads updates. However, to apply updates, users need to click the Update button at the top right of the browser and then relaunch it. Brave browser updates work the same way as Chrome since Brave is Chromium-based.
Chromebook users should know that Chromebooks ship with an Auto Update Expiration (AUE) date. As of the AUE date, these devices will no longer receive software updates from Google.
Internet Explorer has historically had the most vulnerabilities of any browser. Therefore, it should be avoided.
Browser extensions
Several browser extensions have had vulnerabilities.
Google had to remove a Chrome extension called The Great Suspender, which about 2 million people used. This was due to reports that the extension had been compromised and may have installed malicious code and tracking software on users’ systems.
Cloud software
With cloud software, patching is not necessarily under the control of an individual business. Since many cloud apps are multi-tenant, most vendors quickly patch customer accounts.
Salesforce, a popular cloud CRM vendor, provides proactive security release updates to defend against potential vulnerabilities before they can happen. Customers can choose to apply these before the date they are automatically applied.
Remote access devices
This type of hardware device may need periodic patching.
For example, one of SonicWall’s Secure Mobile Access devices had a critical CVE with its 10.x build version.

Firewalls
Firewalls factor into network security and need to be frequently patched.
Cisco and Palo Alto Networks software update their security software every 15 minutes. Cyberoam’s software is updated every night.
Intrusion protection devices
The software embedded in your network devices requires updates each time the vendor releases new patches.
For example, Cisco’s IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) software needs to be patched regularly.
Patch management software
Ironically, some of the software designed to patch software has itself had vulnerabilities.
In 2021, Kaseya’s VSA had a notoriously exploited vulnerability that affected up to 1,500 SMBs. Solar Winds customers were also victims of a notorious attack.
Ensure the patch management software used within your business has a clean record.
Regularly patching software and devices is one of a business’s best defenses against exploits by hackers and ransomware gangs.
No matter what size, all businesses should have a patching strategy and plan. This should include automating as much of the patching process as possible.