Never have there been more (or better) choices for backing up business data on your computers and other devices. What can be difficult, however, is figuring out what the best option is for your particular business.
Backing up your company information locally and in the cloud has distinct advantages. Additionally, you can use both options concurrently if that works for you. As businesses evolve, they tend to go through various levels of data backup solutions as their needs grow more complex.
To give you an idea of the options for business data backup, we’ve compiled a short list of the various tiers that businesses commonly progress through. None of these options preclude you from using any of the others simultaneously.
1) External USB Drive

One of the quickest and easiest ways to back up critical files is to plug a USB drive into a computer. Many USB flash drives have enough storage to back up the entire hard drive for many laptops.
If you’re willing to spend more, you can get a small solid-state external drive with anywhere from 500 gigabytes to several terabytes of storage. There is also no shortage of programs for both macOS and Windows to automate the backup process.
Advantages: USB flash drives are inexpensive, portable, and easy to use. Most are durable and will survive the odd drop or accidental dunk.
Disadvantages: USB backup is a single-user solution that doesn’t scale for multi-user scenarios. As convenient as a USB flash drive is, it’s easy to lose if you’re not careful.
2) Desktop Cloud Backup
Entry-level cloud backup is where many businesses start with backup solutions. Services like Dropbox, Carbonite, and Google Drive are all excellent offerings. Each offers a cloud backup solution that ensures that your files will be recoverable if your desktop or mobile device is lost, stolen, or destroyed.
A cloud backup service provides a robust backup solution for many small businesses.
Advantages: No physical device to keep track of, and you’ll get far more storage space than what’s available on inexpensive USB drives. Your information will be accessible from anywhere you have an internet connection.
Disadvantages: Backing up individual files and folders doesn’t complete the computer’s restoration. Without internet access, you won’t be able to access your data.
3) Network-Attached Storage (NAS)

Network-attached storage (NAS) is an excellent multi-user local backup solution. NAS is a small server that sits in your office. A NAS server creates a network that users can connect to with valid credentials (username and password). Once connected, users can transfer files to and from the NAS at will.
When you buy a NAS server, you’ll need to purchase both the server and the storage drives, which are separate costs. Most NAS servers have multiple drive bays to add more storage over time.
Many businesses like using NAS because once purchased, there are no monthly fees for cloud storage, and consequently, no third parties are involved in handling data backups. A software backup agent can be installed on users’ computers to automate the backup process.
Advantages: It’s an excellent multi-user solution. There are no recurring monthly fees; more storage can be added if needed.
Disadvantages: If your NAS is destroyed and you don’t have a secondary backup solution, you lose all your data.
4) Offsite Business Data Backup

Offsite data backup is similar to but distinct from cloud backup services. It involves putting copies of your data on physical media, like tapes or drives, and sending them to another location for safekeeping.
In a disaster where your business’s location is compromised or destroyed, you can have physical backups sent to you from your offsite storage provider. Unlike cloud storage, you cannot access your stored data daily.
With high internet speeds, physically transporting media offsite is rare these days.
Advantages: There is a recovery option in the event of a disaster.
Disadvantages: A physical drive or tapes must be shipped back to you. Recovery takes a while. Applications and services aren’t covered.
5) Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery (BCDR)
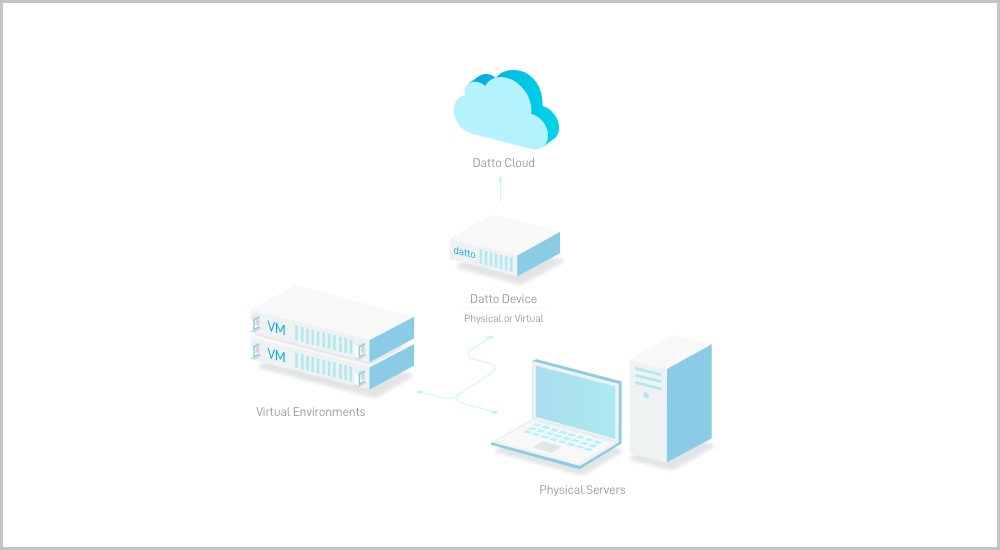
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) is a cutting-edge backup technology solution. With BCDR, users can be up and running again with little downtime should there be a disaster or large-scale data loss from a ransomware attack.
BCDR providers, like Datto, offer solutions to companies that combine physical devices, cloud storage, and virtualization. This type of solution continuously backs up your entire work environment.
Users can be back up and running minutes after any failure or disaster. A BCDR solution includes access to all files, applications, and services without reinstalling or reconfiguring servers or desktops.
Advantages: Replication, offsite backup, and immediate recovery.
Disadvantages: The most expensive of all the options listed.
A robust business data backup strategy is not just a safeguard but a necessity for ensuring continuity and resilience. Organizations can protect themselves against data loss, downtime, and potential revenue disruption by implementing reliable backup solutions and regularly testing their effectiveness.
Investing in a comprehensive data backup plan secures your company’s critical information and provides peace of mind, enabling you to focus on growth and innovation. Don’t wait for a data disaster to strike—take proactive steps now to protect your business.


